In Swift, variable must have value. Because swift wants to ensure safety from run-time error, swift do not allow NULL in variable.
Alternatively, to deal the situation of NULL, swift supports Optional Type.
Optional Type
“Optional” is the expression which can not have value, or have value.
Optional is expressed as Optional<Type> and it can be shorten as ?
So, usually we use ?. Below is the example using optional variable.
var fruit: String? = "apple"
print(fruit)
fruit = nil
print(fruit)
Here is the result.
Optional("apple")
nil
It took long time to fully understand whole concepts. I explained it below.
It is easy to understand if you understand optional type as a box.
Now, we will input or output the value from the box.
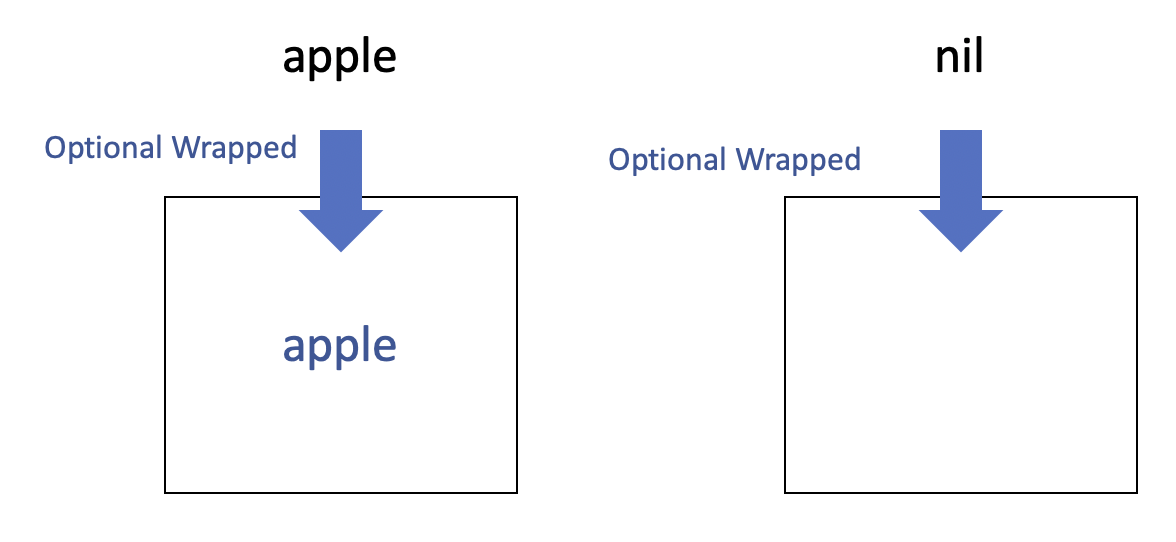
image description.
we call it Optional wrapping
If you input nil, then the box remained empty.
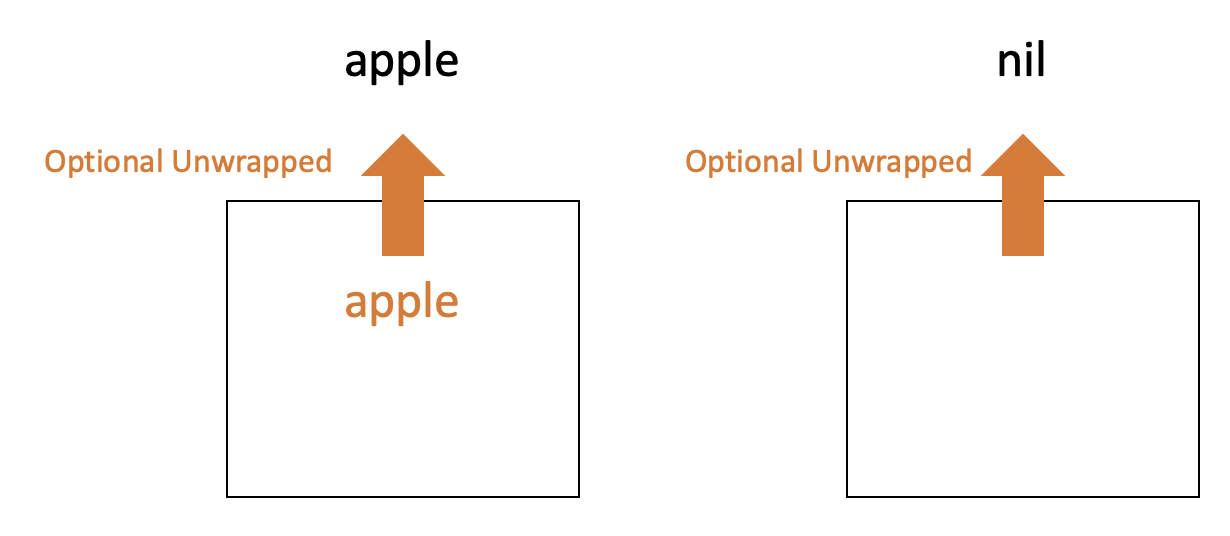
Of course we can abstract apple and nil from boxes, which is called Optional unwrapping
if you output from the empty box, then it gives nil.
So, it should be checked if the value is exist or nil before unwrapping optional.
var fruit: String? = "apple"
if let fruitVal = fruit {
print("Fruit is \(fruitVal)")
} else {
print("Fruit is nil")
}
Optional unwrapping is able only if nil type is checked, but we also can forcing unwrap without that process like as below.
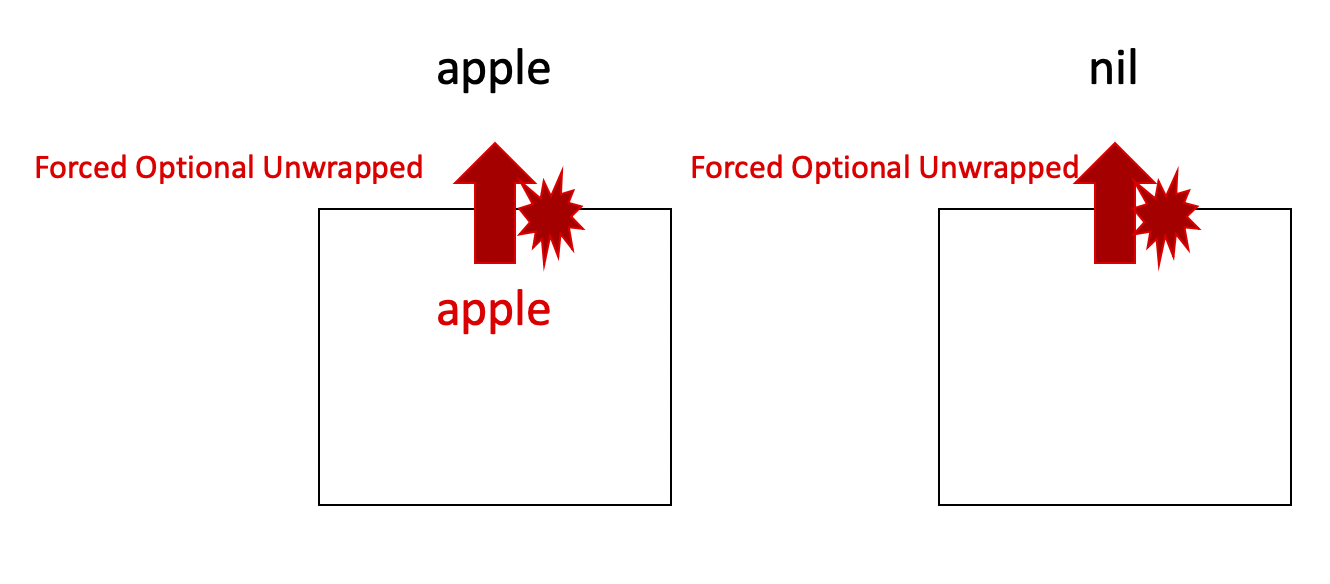
If we use ! after variable, then we can get out of the value from box forcefully.
Overally, I explained the concept with box images. I hope you understand the concept.
We studied optional concepts until now, then how do we abstract value from that box?
There are serveral ways to abstract value from box(unwrapping optional).
Serveral ways to unwrap optional
Indeed, I introduced Optional Binding and Forced Unwrapping a little. However, I should deep dive into their details and other ways ass well.
Optional Binding
This code is Optional Binding which assigns the value from optional variable to other variable.
If fruit is nil, then it excutes else statement.
We call it optional binding because value is binded only if the value is not nil.
var fruit: String? = "apple"
if let fruitVal = fruit {
print("Fruit is \(fruitVal)")
} else {
print("Fruit is nil")
}
Optional Chaining
For explaination, I referenced the code from yagom’s blog
What if we should check multiple optional type?
From the code below, we should make many if statement for each type check.
It is not readable, so swift supports other function(Optional Chaining) for this case.
Optional Chaining is expressed as ?..
Because we chained optional type properties, Logic just need an if statement.
Example Class
class Person {
var name: String
var job: String?
var home: Apartment?
init(name: String) {
self.name = name
}
}
class Apartment {
var buildingNumber: String
var roomNumber: String
var `guard`: Person?
var owner: Person?
init(dong: String, ho: String) {
buildingNumber = dong
roomNumber = ho
}
}
Comparision between Optional Binding and Optional Chaining
let yagom: Person? = Person(name: "yagom")
let apart: Apartment? = Apartment(dong: "101", ho: "202")
let superman: Person? = Person(name: "superman")
// When using just Optional Binding
func guardJob(owner: Person?) {
if let owner = owner {
if let home = owner.home {
if let `guard` = home.guard {
if let guardJob = `guard`.job {
print("my guard's job is \(guardJob)")
} else {
print("my guard do not have any job")
}
}
}
}
}
guardJob(owner: yagom)
// When using Optional Chaining
func guardJobWithOptionalChaining(owner: Person?) {
if let guardJob = owner?.home?.guard?.job {
print("my guard's job is \(guardJob)")
} else {
print("my guard do not have any job")
}
}
guardJobWithOptionalChaining(owner: yagom)
yagom?.home?.guard?.job // nil
yagom?.home = apart
yagom?.home // Optional(Apartment)
yagom?.home?.guard // nil
yagom?.home?.guard = superman
yagom?.home?.guard // Optional(Person)
yagom?.home?.guard?.name // superman
yagom?.home?.guard?.job // nil
yagom?.home?.guard?.job = "guard"
Forced Unwrapping
As we see this by images, just get out of the value from the box without type check.
Because Forced Unwrapping can occur runtime error, it is too dangerous.
Just adding ! after variable is so simple.
var fruit: String? = "apple"
print(fruit!)
But the problem is,
when optional has nil in box(own type), it occurs runtime error like below.
fruit = nil
print(fruit!)
Fatal error result.
Fatal error: Unexpectedly found nil while unwrapping an Optional value: file MyPlayground.playground, line 6
Implicitly Unwrapped Optionals
When we think that Logic does not occur runtime error by nil, we use it.
By adding ! after the optional variable, we do not need to consider optional binding or forced unwrapping.
var fruit: String! = "apple"
print(fruit)
fruit = nil
print(fruit)
This is results.
Optional("apple")
nil
Implicitly unwrapped optionals are convienient. However, because we can usually make mistake about nil, swift recommanded to use optional chaining and optional binding.
Conclusion
Swift is the language wich is safe, fast, expressive.
Optional is one of the representative function which shows Swifty.
By checking NULL condition during compile time, we can persuing error safety.
Hope it helps you :)
Reference
- swift3 ) Optional 개념 정리
- Swift Programming 2 by YAGOM